|
Command Activation
| z |
Measure→Circle |
 |
| Keyboard |
Main Menu |
Toolbar |
Definition
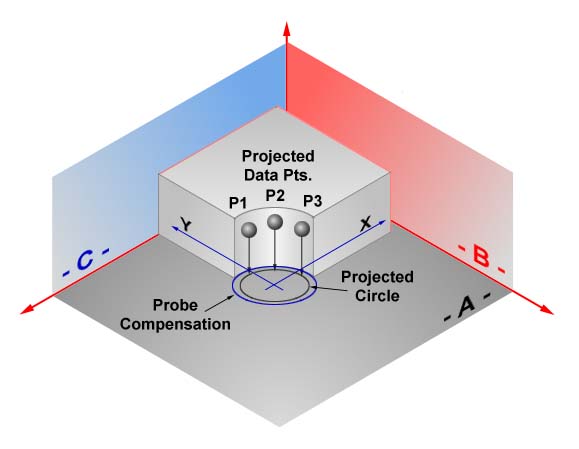
The Circle feature determines the center location and diameter or radius of bores and
bosses whose axes are parallel to a PCS axis. The circle feature will give erroneous
results on skewed bores and bosses. Circle center locations are projected into a PCS base
planes, see figure 1, and are 2D in nature.
 |
|
figure 1, Circle Projection |
To measure bores or bosses, press the Circle key < z > for the default
number of data points as set in System Options. Geomet will then prompt you for the type
of feature being measured, see figure 2. If you have
Auto Direction enabled, this
prompt will not appear.
 |
 |
| figure 2, Selector |
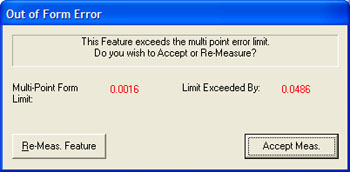
figure 3, Out-of-Form Warning |
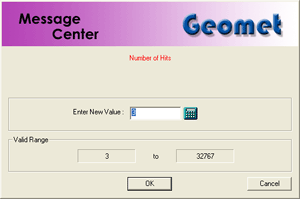
If you required additional data points, you can repeatedly press the Circle key
which increments the required number by one, or press < shift + Z > and you
will be prompted to enter the required number.
 |
|
figure 4, Enter Data Point Count |
Geomet performs a form validation on your captured data points. This function is called
the Multi-Point Error Limit and is controlled by a setting in System Options. In the event
your circle exceeds this limit, Geomet will prompt you whether to accept or re-measure the
feature, see figure 3. If you elect < Re-Measure >, you will be prompted to
capture new data points for the same feature. Note: The Multi-Point Error Limit test
is only performed in the self-teach mode, not during a part program run.
Data Point Spread Caution
Data points used to calculate a circle if not spread around the circle can cause
erroneous results. In the table below, we will use a 3 point circle with one point
.00014" off the nominal value for a 1.00" radius. The results are calculated to
show the error that is part of the reported values.
| Arc (degrees) |
Center error |
Radius error |
| 180° |
0.00014 |
0.00000 |
| 120° |
0.00028 |
0.00014 |
| 90° |
0.00048 |
0.00034 |
| 60° |
0.00104 |
0.00090 |
| 30° |
0.00409 |
0.00395 |
| 20° |
0.00914 |
0.00899 |
| 10° |
0.03549 |
0.03535 |
| 5° |
0.12823 |
0.12810 |
| table 1, Circle
deviations from reduced sweep arc |
As shown above, the center location and radius degrades dramatically as your data
points are taken over a smaller sweep. There are many possible errors when measuring with
CMMs. These include the speed of data point capture, stability of the CMM during motion,
calibration, and repeatability of the probe just to name a few.
Tolerance
Tolerance of Circles is available in Cartesian, Polar or
RFS, MMC and LMC Positional Tolerance formats.
Circles can also be used in the establishment of the Origin in building a
PCS, and if tolerance has been applied, Geomet will calculate the available
Datum Bonus Tolerance, see DBT
Tutorial.
|





